Asynchronous motors, also known as induction motors, possess several significant characteristics and advantages:
Induction Principle: Asynchronous motors operate by energizing the stator windings, which induces the flow of current and energy transfer. During normal operation, they are classified as single-sided excitation motors, where only the stator is connected to the power supply, and the rotor's potential and current are generated through induction. As a result, the motor's air gap magnetic field remains essentially unchanged whether it is running at no-load or under load.
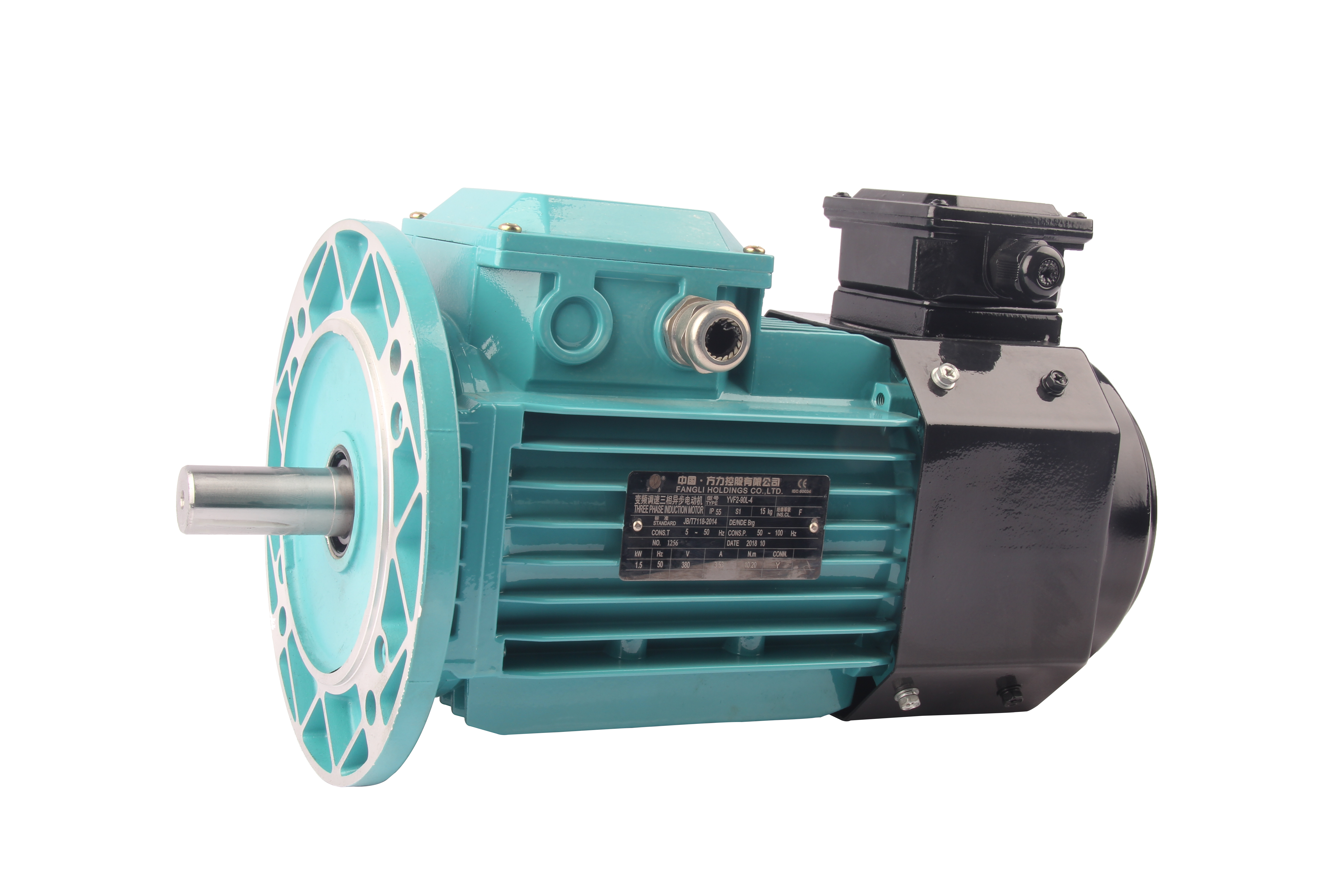
Constant Speed: The rotor winding potential and current frequency of asynchronous motors are not only related to the stator frequency but also directly proportional to the rotor's speed. As long as the power supply voltage and frequency are maintained at their rated values, asynchronous motors typically operate at a constant speed.
Self-Starting: Self-starting is a significant advantage of asynchronous motors. They can initiate rotation from a standstill due to their inherent characteristics. For high-power asynchronous motors, soft-start methods may be employed to reduce the starting current impact. However, with advancements in variable frequency technology and motor technology, particularly in squirrel-cage motors, starting is no longer an issue.
Slip Characteristics: Asynchronous motors exhibit unique slip characteristics, where the actual speed differs from the synchronous speed, described by the slip ratio. Due to manufacturing processes and material variations, even motors with identical specifications may have slight speed differences. Therefore, this characteristic may need to be considered in applications requiring precise speed consistency. Synchronous motors are not affected by such issues.
To achieve speed control of asynchronous motors, several methods can be employed:
Variable Pole Speed Control: Speed control with fixed speed levels can be achieved by adjusting the motor's pole numbers, providing discrete speed options but not continuous speed control.
Variable Frequency Control: Continuous speed control is achieved by changing the power supply frequency. Common series of small to medium-sized variable frequency control motors include YVF, YZP, and YGP, among others.
Adjusting the Slip Ratio: Some motors, such as wound rotor motors, can achieve minor speed adjustments by modifying rotor resistance.
To learn about Asynchronous motors, please visit https://www.cnfangli.com/blogs


 English
English German
German French
French Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Portuguese
Portuguese Ukrainian
Ukrainian Arabic
Arabic Italian
Italian Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian Greek
Greek Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Macedonian
Macedonian Malay
Malay Maltese
Maltese Norwegian
Norwegian Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Romanian
Romanian Serbian
Serbian Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Urdu
Urdu Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Yiddish
Yiddish